In order for the potential of Wi-Fi 6 wireless solutions to be fully realized, the cable system to which the access points are connected must be correctly designed and installed. It is important to consider a number of factors, including remote power supply.
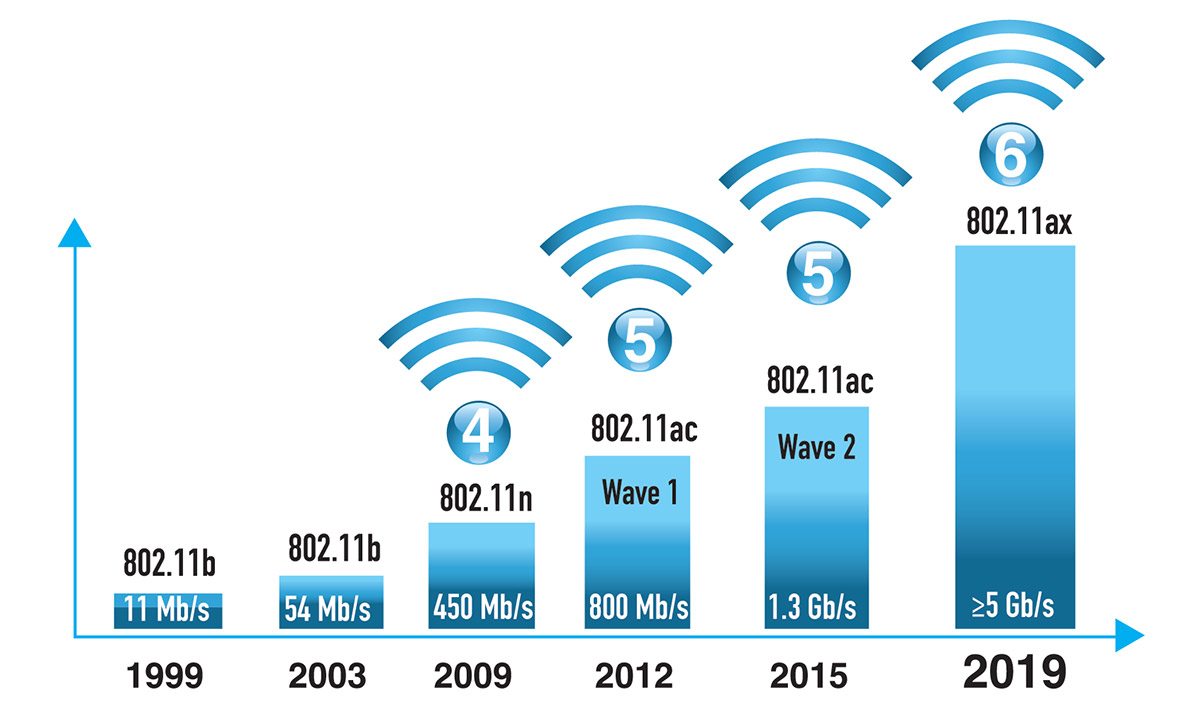
People are using more and more mobile and portable devices – smartphones, tablets, laptops. To support business applications, watch Ultra HD Guest wifi solutions videos and multimedia content, they increasingly need fast Wi-Fi. To do this, you need to connect productive wireless equipment to the local network and make sure that there are no bottlenecks and bottlenecks in the system. The resulting system should be high-performance and provide a quick response. The new generation of technologies, known as Wifi6 wireless solutions (802.11ax), significantly increases the throughput of wireless systems and supports speeds above 5 Gb / s. Increasing throughput, system performance, density of devices in the service area; response time is reduced; longer battery life.
The full potential of Wi-Fi 6 Wifi solution can be fully realized only when the cable system to which the access points connect is correctly designed and installed. When designing a cable system and choosing a transmission medium for connecting Wi-Fi 6 wireless equipment, a number of factors must be taken into account.
Wi-Fi High Speed Support
Wi-Fi 6 technology supports speeds above 5 Gb / s (Fig. 1), and this significantly narrows the choice of possible environments for cable segments between network nodes. In WAP (Wireless Access Point) access points made using Wi-Fi 6 technology, not one port is used to connect to the Ethernet network, as before, but two, and at least one of them must support 2.5 or 5 Gbit / s from. As Wi-Fi 6 technology develops, there will be a need to support speeds above 5 Gb / s. If the existing cable infrastructure does not provide 10-gigabit transfer speeds, then at least two 5-gigabit connections are required for one Wi-Fi 6 access point. At the same time, the future need for two 10-gigabit connections is already visible, because wireless technologies will continue to improve.
All this means that high-performance active equipment will be used in the system, and the cable transmission medium should provide a bandwidth of at least 10 Gb / s, either over twisted pair cable or over multi-mode optical fiber, both in horizontal subsystems and in highways. Otherwise, it will not be possible to implement Wi-Fi 6 Hotel wifi solution .
Each WAP Wi-Fi 6 access point should be supplied with two cable segments of class EA / category 6A, counting on connecting to two Ethernet ports – this is the only way to ensure the necessary transmission speed for various device configurations.
Powering Wi-Fi devices 6
Another important aspect is the power supply to the Wi-Fi 6 wireless access point. Signaling of Wi-Fi 6 radio chips is much more complicated than in the equipment of previous generations, it requires more powerful power. Each Wi-Fi 6 access point needs to be provided with either a local connection to a DC power source or a 30W PoE Type 2 remote power supply. But when remotely powered by PoE Type 2, each pair carries 600 mA, which causes the cable bundle to heat up. The temperature rise can reach 10 ° C compared to the ambient temperature. Cloud managed wifi solutions Heating is accompanied by an increase in the number of bit errors, which leads to a decrease in performance. In addition, when the equipment is turned off “live”, an electric arc discharge occurs.
When choosing a cable environment, it is strongly recommended that shielded cable solutions be preferred because they are resistant to the temperature rise typical of PoE applications. You should choose cable systems that provide reliable operation and mechanical strength at temperatures up to 75 ° C – they are capable of supporting PoE Type 2 power supply and operation over the entire operating temperature range from -20 ° C to 60 ° C. Shielded cable solutions of categories 6A and 7A demonstrate the highest resistance to heat and in such conditions support transmission in longer channels. Such systems make it possible to bundle more cables into bundles without exceeding the permissible temperature increase. In addition, the use of switching equipment that complies with IEC 60512-99-001,
Flexibility in designing and deploying WAP access points
When creating a cable infrastructure for reliable support for Wi-Fi 6 solutions, you must also take into account the connection speeds of network switches, servers and devices available on the market today, as well as strategies for updating them, developing future wireless technologies and ensuring reliable operation of systems.
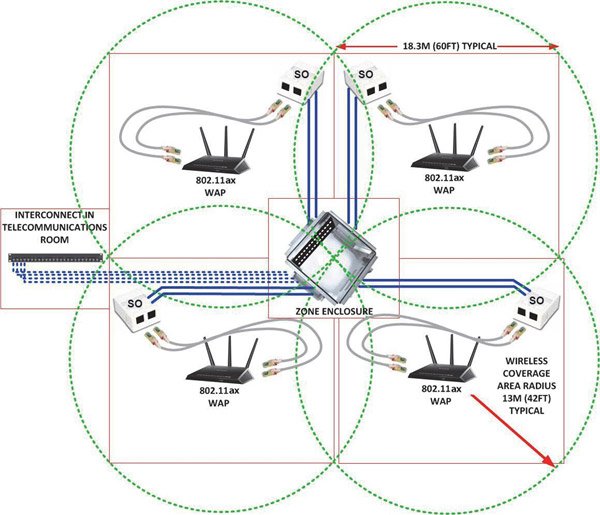
Class EA / Category 6A cabling systems based on the zonal approach and service concentration points (SCPs) in zone cabinets provide the required port density and support for 2.5 / 5GBASE-T applications per WAP access point. The same systems guarantee the possibility of efficient use of ports when connecting 10GBASE-T equipment in the future.
The zonal approach provides the necessary flexibility and allows easy configuration changes in service areas. It is characterized by stock availability and consideration of the needs of future technologies, including the use of several 10GBASE-T segments for connecting devices. You can always add WAP access points to your existing wireless network to improve coverage. This practically does not cause inconvenience to the inhabitants of the building, since there are always redundant ports in the zone subsystems. Siemon experts recommend that each zone cabinet service a zone with a radius of 13 m
The number of ports (cable terminations) at the service concentration point varies from 24 to 96, depending on the office or other environment in the building, the adopted automation level, type of ceiling lighting, type and number of applications – Wi-Fi, security systems, CCTV, access control, other building automation equipment. The relative position of the SCP points may be based on a mesh structure, a configuration for extended segments, or a hexagon structure.









