
Quite often there is a situation when you want to organize a seamless coverage of a large area and to manage the wireless network with a large number of access points. guest wifi solutions Let’s talk about how to optimally implement the project: where to start, what parameters to consider, how to set up the equipment and where the trick can wait. As a living example, choose our enterprise-class access points and network controllers.
At the first stage, it is necessary to decide what equipment and in what quantity will be needed to build the network. In this case, it is not only about controllers and access points. wifi6 wireless solutions A wireless network cannot function without its wired infrastructure. Therefore, at this stage it is necessary to take into account the wire segments, since it is quite likely that they will have to be modernized.
How to determine if the existing wired infrastructure is suitable for your wireless network? First, there should be enough free ports on the access switches to connect wireless equipment. In addition, the modern IEEE 802.11N / AC network provides subscribers with quite high access speeds, which leads to tougher speed requirements for wired interfaces, as well as performance of the wired part of the network as a whole.
Secondly, to optimize the power supply circuit, modern access points can receive power not only from an external source, but also through a network cable using PoE technology outdoor wifi solutions (IEEE 802.3af or 802.3at, depending on the model) – but in order for this to work, access switches must also support this technology.
Third, access switches must be managed and supported by virtual networks (VLANs), which is necessary when wireless equipment uses multiple SSIDs. Fortunately, almost all switches used in the corporate segment can do this. Finally, you may have to make changes to the SCS – it depends on the total number of access points and their installation sites wifi solution.
But how to understand how many access points you need to install? At a minimum, to pay attention not only to the general plan of the premises, but also to places of mass gathering of users, as well as the number of people who can simultaneously use the connection in each of them. At the same time, places of mass gathering are not only conference halls or work rooms of employees, but also shopping centres, educational institutions, hotel lounges, elevators, cafes and restaurants and other areas that are less obvious at first glance. In fact, here, competent radio frequency intelligence is indispensable. And here we have the opportunity to help our customers do radio planning and conduct radio frequency surveys, for which we have the appropriate hardware and software. hotel wifi solution However, a rough estimate of the number of access points depending on the density of users can be made immediately.
Need of Wireless Controller
Do you need a controller if you have only a few access points? The answer to this question is a little more complicated than it might seem at first glance. The architecture of modern wireless networks has changed, and now a couple of access points will be enough only for a very small network. Previously, at each site of the network coverage was provided by one access point with a transmitter at maximum power. In modern networks it is recommended to make a distributed installation of two or more access points whose transmitters are not used at full capacity. guest-wifi solutions This architecture allows you to fully utilize the wired infrastructure, as well as to achieve higher client connection speeds through the use of complex modulations, available only with close mutual location of the access point and the wireless client.
The modern wireless network architecture also provides additional insurance in case of equipment breakdown: if one access point fails, its functions will temporarily be taken over by neighbouring wireless devices, which would be impossible if it were alone responsible for the site.
Using the 5GHz band allows you to unload the 2.4 GHz problem frequency, however, the higher frequency signal is absorbed more by various obstacles located between the receiver and the transmitter, which in some cases significantly reduces the coverage area of the network operating at 5GHz, and again brings us to the need to increase the grouping of access points at the facility.
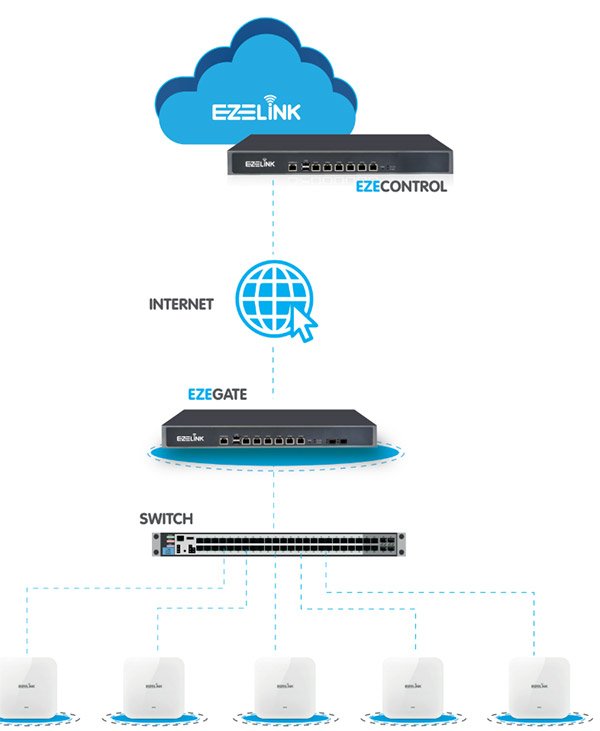
The procedure for deploying a wireless network is quite transparent and consists of several simple steps. We should start with the preparation of the network infrastructure for the introduction of the wireless segment. For definiteness, we assume that it is necessary to provide coverage with a wireless network at the facility, which is one building or a group of closely located buildings connected by a local area network. EZELINK wireless equipment has the ability to remotely connect access points to the controller, however, for simplicity, we assume that all connections are made within one local cloud managed wifi solutions network.
We decided to somewhat complicate the task of pilot implementation and use the existing wired infrastructure built on the basis of equipment from another manufacturer, as well as to place the controller and access points on different subnets.
Network traffic patterns
Depending on the relative position and settings of the wireless controller, access points and the wired network segment, several typical patterns of user traffic are possible. They need to be considered when designing a wireless network to avoid overload in the wired segment.
Access points connect directly to the wireless controller
This model can usually be found in small wireless networks where the number of access points is relatively small. Access points can be connected either directly to the ports of the wireless controller or to auxiliary switches with or without PoE support.
Regardless of whether the controller performs the switching or routing of user traffic, the link between the switch and the controller may be a bottleneck.
The controller acts as the default gateway for wireless networks.
This model does not regulate the mutual arrangement of the wireless controller and access points in the network. The fundamental fact is the configuration of network equipment and client devices, in which the controller acts as a default gateway for wireless clients. In this case, the link between the switch and the controller will also be overloaded.
The default gateway functions are assigned to a router or L3 switch.
This model is optimal from the point of view of performance, since the wireless controller is completely excluded from the transmission path of user traffic. Access points essentially act as bridges, associating a wireless SSID with a VLAN in a wired segment. All further traffic processing is done by wired switches and routers.
EZELINK wireless controller is capable of routing traffic for two Gigabit Ethernet ports at an environment speed in Full Duplex mode, fully utilizing the resources of both processor cores and users will be able to get a total of 2 Gbit/s large packets in total.
It is impossible not to notice that the traffic switching is carried out by the controller practically without using the central processor, which allows using all five Gigabit Ethernet ports in L2 mode at the speed of the environment, while leaving the central processor resources free for other tasks.
The AC1750 Access Point provides users with a maximum theoretical speed of 750 Mbps in the 2.4 GHz band and 1.3 Gbit/s in the 5 GHz band. In practice, when using the AC1750 model in the 2.4 GHz band, the total speed of simultaneous transmission of user data in both directions is about 260 Mbit / s. For the 5 GHz band, this value is 620 Mbps.
Thus, in practice, one access point AC1750 will be able to transmit about 900 Mbit / s of traffic to a wired network when wireless clients are connected to both frequency bands. These speeds should be considered when building or updating a wireless network, reducing the oversubscription in the wired segment whenever possible.
Firmware update
The wireless controller and access points are ready to work
right out of the box, but we always strongly recommend updating the software
that is pre-installed on the devices. The new firmware will not only fix the
detected inaccuracies in the code, but also add new features. For example, one
of the most interesting new products for our equipment will be support for
cloud management, which allows you to centrally manage several wireless
controllers at once. This option will be in demand in the case of very large or
distributed objects. We are also implementing IPv6 support, which will allow us
to use our wireless equipment in new generation IP networks. For network administrators,
we have added support for the SNMP protocol, with the help of which it is
possible to centrally control devices and collect statistics on the use of the
controller and access points. As well as command line support.
When building a wireless network on a large or complex site, you need a lot of wireless access points to provide a continuous coverage area. They are managed (in FIT mode) in this case using a wireless controller. To update their firmware, you also need to use a controller. A centralized change of firmware versions of access points is performed using the controller’s web interface, where you need to download a file containing the new firmware version, as well as specify the start time for the update. Also here you can view a list of access points that it affects.
The ability to centrally update is especially useful for the wireless controller, since this model supports up to 500 access points at the same time, which makes manual replacement of firmware on a tracking object almost impossible.
Since our range of equipment is constantly updated, after the release of a new model it is necessary to update the database of supported devices on the controller in order to expand the list of controlled equipment.
Installation and configuration of EZELINK equipment is extremely simple, and a large number of changeable parameters allows you to flexibly configure the network in accordance with all the wishes of the customer. Below we list the key features of our products that we consider to be the most popular and relevant when building large-scale networks:
Automatic detection and centralized management of access points;
- The ability to locally and remotely locate access points
- Load balancing
- Support of local switching of user traffic by access points
- Unified customization
- PoE support
- Support for multiple SSIDs
- Various user authentication methods
- Flexibility and scalability of the solution








